Umbraco 17 Background Jobs
Introduction
Modern web applications rely heavily on background tasks to keep systems reliable, performant, and maintainable. Many of these tasks need to run automatically at fixed times or at regular intervals, without any user involvement.
Traditionally, this requirement has been handled using server-level cron jobs. While cron jobs are effective, they can become difficult to manage, monitor, and scale, especially in cloud-based or load-balanced environments. Configuration often lives outside the application, making deployments, debugging, and observability more complex.
With Umbraco 17, scheduling background tasks becomes much simpler and more developer-friendly through Recurring Background Jobs. This built-in feature allows developers to define, register, and manage scheduled tasks directly within Umbraco, without relying on external schedulers or infrastructure-level cron jobs.
In this Article, we will explore how cron-like scheduling works in Umbraco 17, understand what Recurring Background Jobs are, and discuss when and why they should be used.
What Is Task Scheduling?
Task scheduling is the process of automating tasks so that they run at predefined times or intervals.
Common Use Cases
Some everyday examples include:
- Sending scheduled or batch emails
- Cleaning up logs, cache or temporary data
- Syncing data with third-party systems
- Running periodic maintenance or health-check tasks
Instead of triggering these tasks manually, scheduling ensures they run automatically, consistently, and without human intervention.
Task Scheduling in Umbraco 17
Now that we understand task scheduling in general, let us see how Umbraco 17 approaches it.
With Umbraco 17, we have built-in support for scheduling background tasks using the IRecurringBackgroundJob interface. This approach removes the dependency on traditional cron jobs and allows scheduling to be handled entirely within the CMS itself.
Key Features
1. Built-in Scheduling Support
Developers can define recurring background jobs directly in Umbraco using IRecurringBackgroundJob, without additional infrastructure configuration.
2. Flexible Scheduling
Jobs run based on a TimeSpan, allowing:
- Interval-based execution
- An optional delay before the first run
3. Automatic Execution
Once registered, jobs run automatically based on their defined schedule. No manual triggers, external schedulers, or Windows services are required.
Why Choose Recurring Background Jobs in Umbraco 17?
Recurring Background Jobs in Umbraco 17 are designed specifically for CMS-driven applications. They provide a structured, reliable, and Umbraco-aware way to run scheduled tasks without relying on external cron jobs or custom infrastructure.
Dependency Injection Ready
Recurring Background Jobs fully support dependency injection, allowing you to easily inject both Umbraco core services and custom application services, such as:
- IContentService
- ILogger
- Custom domain or integration services
Because jobs are resolved through Umbraco’s dependency injection container, they follow the same patterns as the rest of your application. This keeps background job logic clean, modular, testable, and easy to maintain over time.
Scoped Execution with Umbraco Context
Each recurring background job executes within an ICoreScope, which ensures:
- Safe and consistent database access
- Proper transaction management
- Protection against partial updates or data corruption
This is particularly important for background tasks that interact with Umbraco content, media, members, or custom database tables.
Lifecycle Awareness
Recurring Background Jobs are fully aware of Umbraco’s application lifecycle. They respect:
- Application startup
- Application shutdown
- Deployments and restarts
This prevents jobs from running unexpectedly during deployments or while the application is shutting down, which is a common risk when using external cron jobs.
Easy and Centralized Registration
Jobs are registered through Umbraco’s dependency injection system using a composer. Once registered:
- No additional configuration is required
- Scheduling is handled automatically by Umbraco
- Execution, lifecycle management, and scoping are managed for you
This centralized approach keeps all scheduling logic inside your Umbraco codebase, making it easier to understand, maintain, and deploy across environments.
Built Specifically for Umbraco
Unlike generic background processing solutions, Recurring Background Jobs are built with Umbraco in mind. They integrate seamlessly with Umbraco services, database scopes, and lifecycle events, making them the safest and most reliable option for Umbraco-specific background tasks.
Let's Implement Recurring Background Jobs in Umbraco 17
Task scheduling in Umbraco 17 involves two main steps:
- Creating a class that implements IRecurringBackgroundJob
- Registering it with Umbraco using a composer
Important Properties of IRecurringBackgroundJob
- TimeSpan Period: Defines how often the job runs
- TimeSpan? Delay: Optional delay before the job runs for the first time
- Task RunJobAsync(): Contains the logic that executes every time the job runs
- EventHandler PeriodChanged (Optional): Used when the job’s execution interval needs to change dynamically
This design keeps scheduling logic explicit, predictable, and easy to reason about.
Example Implementation: DoSomeBackgroundJob
public class DoSomeBackgroundJob(IContentService contentService, ICoreScopeProvider scopeProvider : IRecurringBackgroundJob
{
private readonly IContentService _contentService = contentService;
private readonly ICoreScopeProvider _scopeProvider = scopeProvider;
public TimeSpan Period => TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1);
public TimeSpan Delay => TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30);
public event EventHandler PeriodChanged;
public Task RunJobAsync()
{
using ICoreScope scope = _scopeProvider.CreateCoreScope();
int numberOfThingsInBin = _contentService.CountChildren(Constants.System.RecycleBinContent);
if (_contentService.RecycleBinSmells())
{
_contentService.EmptyRecycleBin(userId: -1);
}
scope.Complete();
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
public class DoSomeBackgroundJobComposer : IComposer
{
public void Compose(IUmbracoBuilder builder)
{
builder.Services.AddRecurringBackgroundJob();
}
}
Step 3: Run the Job
After restarting the application, the job will start running automatically based on the configured schedule. Once the job is created and registered, Umbraco takes care of execution. No additional configuration or manual triggering is required.
Introduction to IHostedService
When working with .NET, background tasks are commonly implemented using IHostedService.
What Is IHostedService?
IHostedService is a .NET Core interface used for running background services such as:
- Polling jobs
- Long-running processes
- Background workers
While powerful, this is a generic .NET solution and is not specifically designed for Umbraco-based applications.
Umbraco Recurring Jobs vs IHostedService
| Feature | IRecurringBackgroundJob | IHostedService |
| Umbraco Integration | Native | Manual |
| Scheduling Support | Built-in | Custom |
| Lifecycle Awareness | Yes | Partial |
| Scoped Database Access | Yes | Manual |
| Best For | Umbraco-specific tasks | Generic .NET tasks |
For Umbraco-based projects, IRecurringBackgroundJob is usually the preferred and safer option.
Things to Keep in Mind
When working with background jobs, consider the following best practices:
- Be cautious in multi-environment or load-balanced setups
- Avoid long-running or blocking operations
- Ensure jobs are idempotent
- Use proper logging and error handling for monitoring
These practices help prevent unexpected issues in production environments.
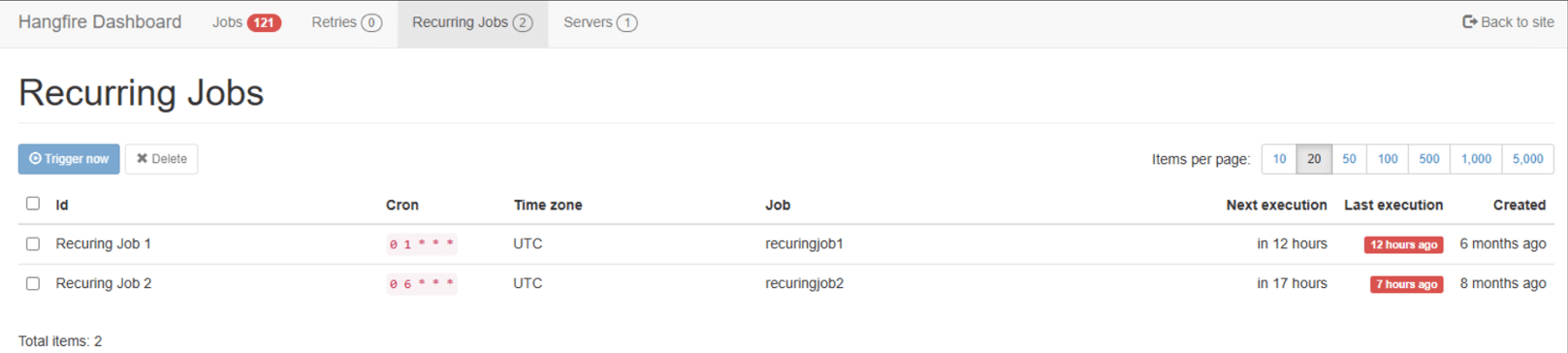
Helpful packages to view and manage background job dashboards in the Umbraco backoffice
The Umbraco Marketplace also offers packages that simplify job scheduling without requiring extensive custom code.
One popular option is Cultive.Hangfire, which provides:
- Advanced job configuration options
- A user-friendly dashboard to monitor and manage background jobs
Conclusion: Umbraco 17 Background Jobs
Umbraco 17 provides a clean, modern, and CMS-native approach to cron-like scheduling through Recurring Background Jobs.
Instead of relying on external cron jobs, developers can now:
- Schedule tasks directly within their Umbraco implementation
- Leverage full dependency injection support
- Maintain complete control over job execution and application lifecycle
This approach simplifies background processing while keeping everything within the Umbraco ecosystem. If you are planning to implement task scheduling or background automation in Umbraco 17, Recurring Background Jobs are the way forward. And if you need expert guidance, we at Giriraj Digital – The Industry Leading Umbraco Gold Partner, can help you design and implement scalable Umbraco solutions tailored to your business needs. Let's connect
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the alternative to cron jobs in Umbraco 17?
Umbraco 17 provides Recurring Background Jobs, a built-in CMS-native alternative to traditional cron jobs.
How do I schedule recurring tasks in Umbraco?
You implement IRecurringBackgroundJob and register it using a composer. Umbraco handles scheduling automatically.
Are Recurring Background Jobs safe in production?
Yes. They run inside Umbraco scopes, respect application lifecycle events, and support dependency injection.
Is there a dashboard to monitor jobs?
Yes. Packages like Cultive.Hangfire provide a backoffice dashboard for job monitoring.
Most Popular blogs
Umbraco 13 to 17 Upgrade Guide
10 Mins read
Top 5 Umbraco Hosting Options
4 Mins read
What’s New in Umbraco 17 ?
7 Mins read
Umbraco vs Optimizely
5 Mins read
Why Umbraco is the right choice for your eCommerce needs ?
3 Mins read
Why Choose Umbraco over Sitecore?
6 Mins read
Giriraj Digital Becomes Umbraco Gold Contributing Partner
3 Mins read
Is Umbraco the Right CMS for Your Business in 2026?
3 Mins read
Nikhil Joins the Umbraco CMS Advisory Board 2025
2 Mins read
Umbraco Education Program India
5 Mins read
The Detailed Guide to Hiring Umbraco Developers from the Outsourcing Company!
4 Mins read
How Umbraco health checkups will help your site going smooth & appeals customers
3 Mins read

Join 1500+ people for our free Newsletter
Sign up now to receive exclusive updates, industry insights, and special offers directly to your inbox.







