Umbraco Content Delivery API
A Complete Guide for Headless & On-Premises Projects
Modern digital platforms rarely live in a single place anymore. Websites, mobile apps, kiosks, CRMs, and even IoT devices all need access to the same content to be fast, secure, and structured. This is where the Umbraco Content Delivery API becomes a game changer.
In this article, we will walk through what the Umbraco Content Delivery API is, why it matters, and how to set it up step-by-step in an on-premises headless project, followed by configuration options, endpoints, and real-world usage patterns.
What Is the Umbraco Content Delivery API?
The Umbraco Content Delivery API is a REST-based, read-only API designed to expose published Umbraco content to any frontend or external system.
Instead of rendering Razor views inside Umbraco, the Delivery API allows you to:
- Build headless websites
- Power React, Angular, Vue, or mobile apps
- Share content with external platforms
- Decouple content management from presentation
In short: Umbraco becomes your content hub, not just your website engine.
Why Use the Content Delivery API?
Using the Delivery API makes sense when:
- You want frontend freedom (React, Next.js, Angular, mobile apps)
- You need multi-channel content delivery
- Performance and scalability matter
- You want a clean separation between editors and developers
- You’re migrating from heavyweight platforms (e.g., Sitecore) to a modern headless architecture
Architecture Overview (Headless Umbraco)
At a high level, the architecture looks like this:
- Umbraco CMS (On-Premises)
Content creation, workflows, publishing - Delivery API
Secure REST endpoints exposing structured content - Frontend Applications
Web apps, SPAs, mobile apps, or third-party systems
Umbraco manages content. Your frontend decides how to render it.
Step 1: Enable Content Delivery API in appsettings.json
By default, the Delivery API is disabled. You must explicitly enable it.
Add the following configuration under Umbraco > CMS:
{
"Umbraco": {
"CMS": {
"DeliveryApi": {
"Enabled": true
}
}
}
}
This tells Umbraco that your project is allowed to serve content via the Delivery API.
Step 2: Register Delivery API in Program.cs
Next, wire the Delivery API into the Umbraco pipeline.
Inside builder.CreateUmbracoBuilder() add:
builder.CreateUmbracoBuilder()
.AddBackOffice()
.AddWebsite()
.AddDeliveryApi()
.AddComposers()
.Build();
Without .AddDeliveryApi(), the API endpoints will not be available, even if enabled in configuration.
Step 3: Rebuild the Delivery API Examine Index
The Delivery API relies on a dedicated Examine index called:
DeliveryApiContentIndex
After enabling the API:
1. Go to Settings and navigate to Examine Management
2. Locate DeliveryApiContentIndex
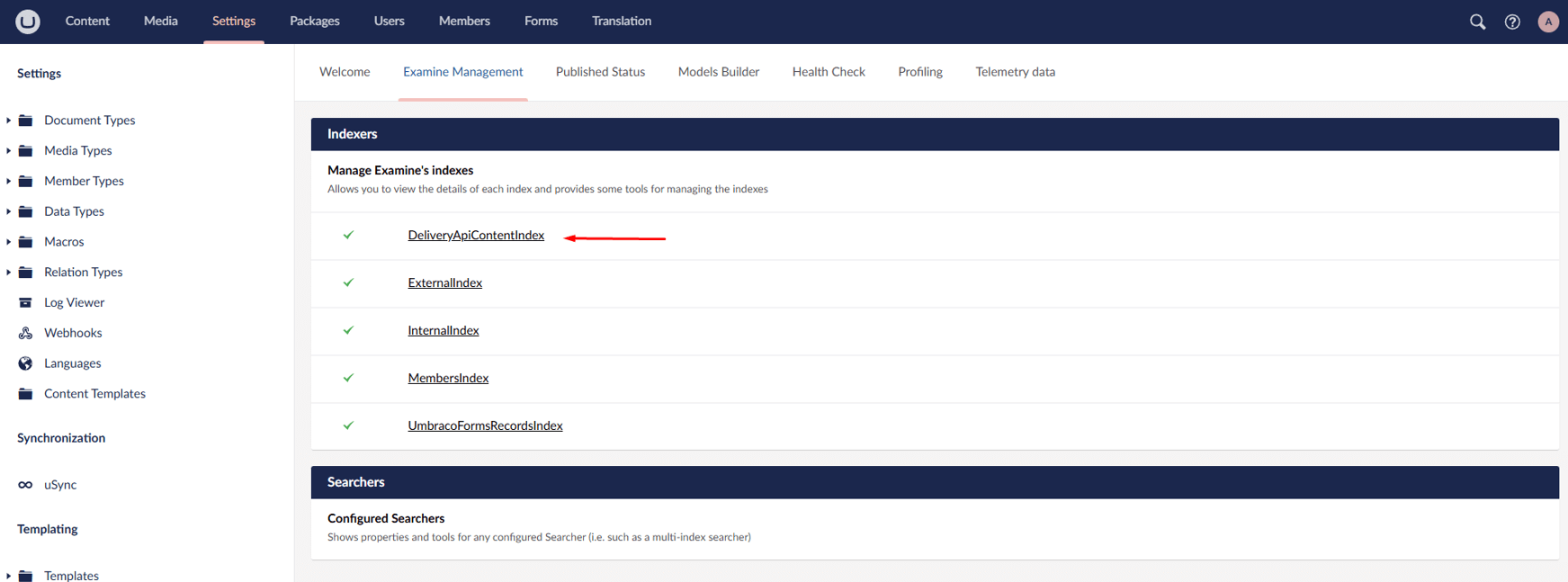
3. Click Rebuild Index
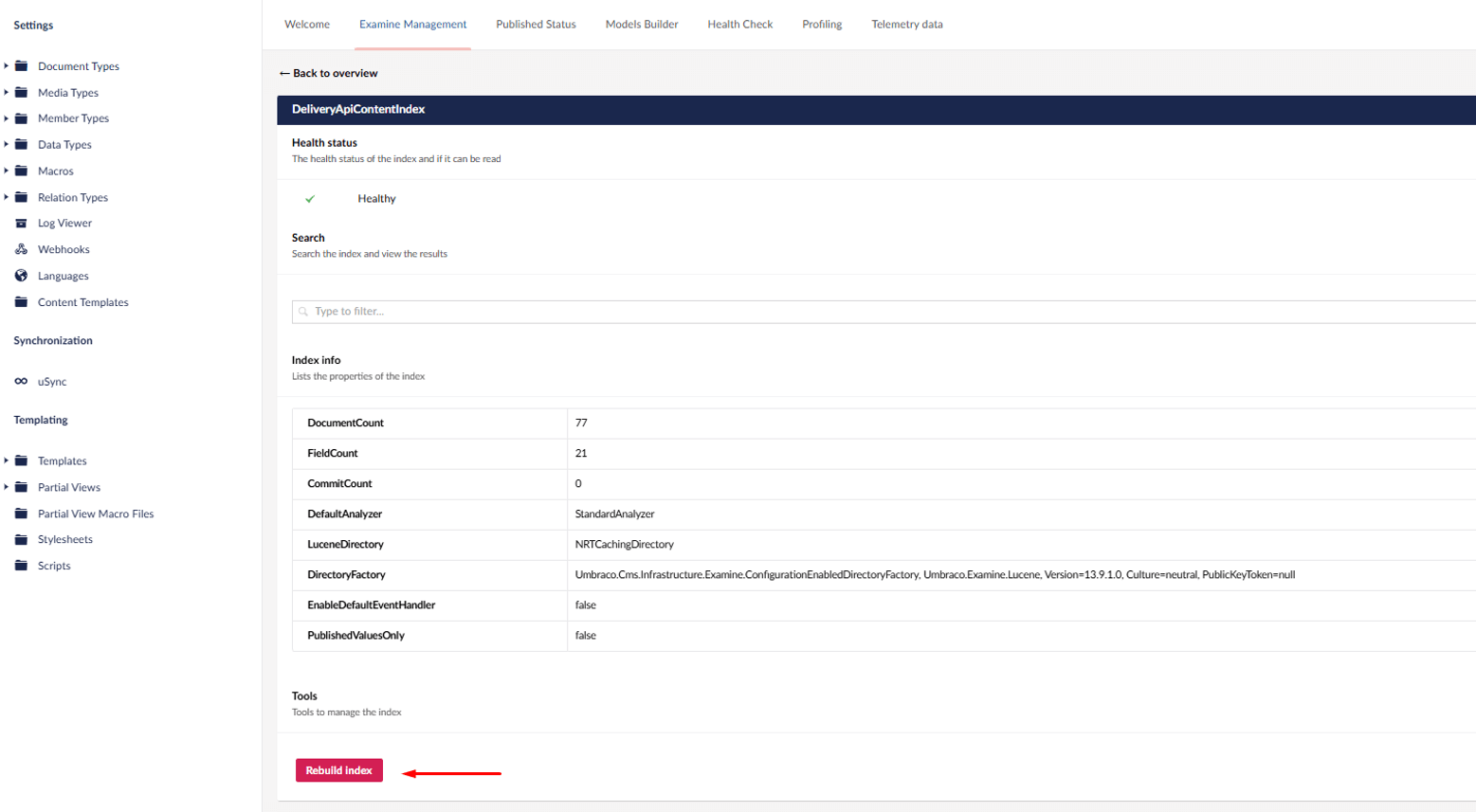
This step is critical. Once the index is rebuild, the API can serve the latest content from the multiple-items endpoint.
Securing & Controlling the Delivery API
Out of the box, the Delivery API is fully open. In real projects, you usually want tighter control.
{
"Umbraco": {
"CMS": {
"DeliveryApi": {
"Enabled": true,
"PublicAccess": true,
"ApiKey": "my-api-key",
"DisallowedContentTypeAliases": ["alias1", "alias2", "alias3"],
"AllowedContentTypeAliases": ["allowedAlias1", "allowedAlias2", "allowedAlias3"],
"RichTextOutputAsJson": false
}
}
}
}
1. PublicAccess
- "true" - Anyone can access content
- "false" - API key required
Recommended
- Public websites set to "true"
- Apps or Private APIs set to "false"
2. ApiKey
Required when PublicAccess is set to false.
Also used for:
- Previewing unpublished (draft) content
- Secure integrations
3. Allowed vs Disallowed Content Types
i.DisallowedContentTypeAliases
- Explicitly blocks content types
- Useful for internal or admin-only content
ii.AllowedContentTypeAliases
- Acts as a whitelist
- If defined, only these types are exposed
- Overrides the disallowed list
Best practice: Always whitelist content types in production
4. RichTextOutputAsJson
- false (default): Returns HTML
- true: Returns structured JSON
JSON output is ideal for React or Native mobile apps, Custom rendering pipelines
Core Delivery API Endpoints
// Retrieve content using its URL
GET /umbraco/delivery/api/v2/content/item/{path}?expand=properties[$all]
//Example:
/umbraco/delivery/api/v2/content/item/blog/my-first-post?expand=properties[$all]
// Perfect for deep linking or cached references.
GET /umbraco/delivery/api/v2/content/item/{id}
// It will be useful for breadcrubms and navigation trees.
GET /umbraco/delivery/api/v2/content?fetch=ancestors:{id}&take=1
GET /umbraco/delivery/api/v2/content?fetch=children:{id}
GET /umbraco/delivery/api/v2/content?fetch=descendants:{id}
GET /umbraco/delivery/api/v2/content?filter=contentType:blogPost
GET /umbraco/delivery/api/v2/content?sort=name:desc
// Essential for performance and scalability.
GET /umbraco/delivery/api/v2/content?skip=10&take=5
Using Umbraco Forms in Headless Mode
Umbraco Forms has its own dedicated Headless API, separate from the Delivery API.
{
"Umbraco": {
"Forms": {
"Options": {
"EnableFormsApi": true
}
}
}
}
// Used to render forms dynamically on the frontend.
GET /umbraco/forms/api/v1/definitions/{formId}
POST /umbraco/forms/api/v1/entries/{formId}
It handles validation and submissions securely.
Best Practices for Production
- Always rebuild DeliveryApiContentIndex after schema changes
- Whitelist content types using AllowedContentTypeAliases
- Use API keys for mobile or private applications
- Cache API responses at the frontend layer
- Avoid exposing utility or system content types
- Version your frontend independently from Umbraco upgrades
Final Thoughts
The Umbraco Content Delivery API transforms Umbraco from a traditional CMS into a modern, headless content platform. Whether you’re building a SPA, mobile app, or multi-channel ecosystem, it gives you the flexibility to scale without compromising editorial experience.
If you are already using Umbraco on-premises, enabling headless delivery is a configuration decision but not a rebuild. That’s the real power of Umbraco.
Thinking about building a headless solution with Umbraco or migrating from a legacy CMS? Our team specializes in designing and delivering scalable Umbraco headless architectures. Reach out to us today to discuss your project and see how the Umbraco Content Delivery API can accelerate your digital roadmap.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Umbraco Content Delivery API?
The Umbraco Content Delivery API is a REST-based API that exposes published Umbraco content for headless use cases such as React, Angular, mobile apps, and external systems.
Is the Umbraco Content Delivery API free?
Yes. The Content Delivery API is included with Umbraco CMS and does not require a paid license.
Can I use the Content Delivery API in on-premises Umbraco projects?
Absolutely. The Delivery API works fully in on-premises Umbraco installations with minimal configuration.
How do I secure the Umbraco Delivery API?
You can secure it using API keys, disable public access, and whitelist specific content types using AllowedContentTypeAliases.
Does the Delivery API support preview or unpublished content?
Yes. When API keys are enabled, the Delivery API can serve draft and preview content securely.
How is Umbraco Forms handled in headless mode?
Umbraco Forms provides a dedicated Headless API for fetching form definitions and submitting entries separately from the Content Delivery API.
Do I need to rebuild indexes after enabling the Delivery API?
Yes. You must rebuild the DeliveryApiContentIndex to ensure the API serves the latest content.
Most Popular blogs
Umbraco 13 to 17 Upgrade Guide
10 Mins read
Top 5 Umbraco Hosting Options
4 Mins read
Umbraco 17 Recurring Background Jobs & Scheduling Guide
9 Mins read
What’s New in Umbraco 17 ?
7 Mins read
Why Umbraco is the right choice for your eCommerce needs ?
3 Mins read
Giriraj Digital Becomes Umbraco Gold Contributing Partner
3 Mins read
Nikhil Joins the Umbraco CMS Advisory Board 2025
2 Mins read
Umbraco Education Program India
5 Mins read
The Detailed Guide to Hiring Umbraco Developers from the Outsourcing Company!
4 Mins read
How Umbraco health checkups will help your site going smooth & appeals customers
3 Mins read

Join 1500+ people for our free Newsletter
Sign up now to receive exclusive updates, industry insights, and special offers directly to your inbox.







